Introduction
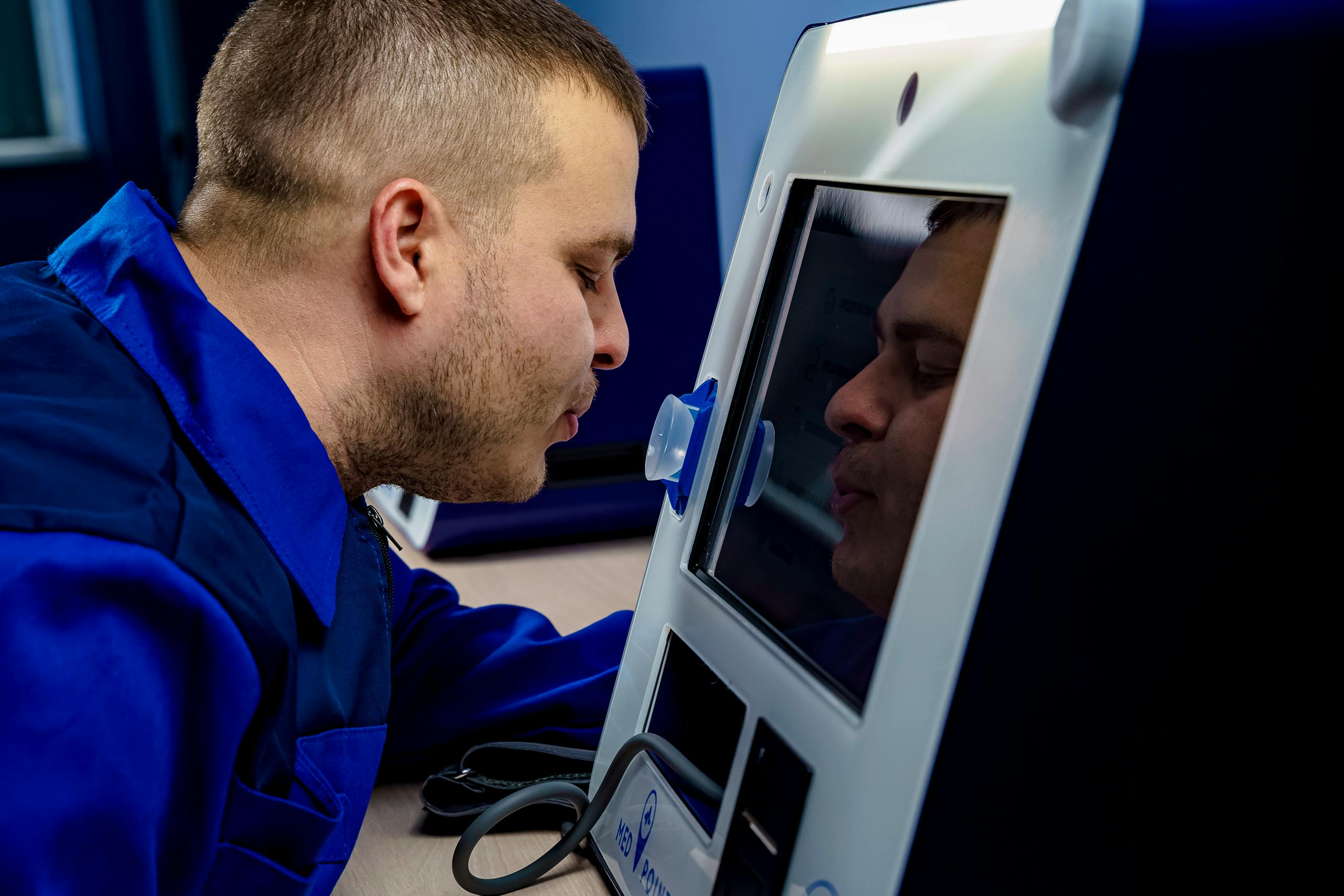
Telemedicine, the remote provision of healthcare services, has emerged as a transformative force in the medical landscape. As technological advancements continue to redefine how we access and receive medical care, telemedicine stands at the forefront, offering convenience, accessibility, and efficiency. This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of telemedicine, exploring its evolution, benefits, challenges, and future prospects.

Understanding Telemedicine
Defining Telemedicine
Telemedicine encompasses the delivery of healthcare services through digital communication technologies, enabling remote diagnosis, consultation, and treatment.
Historical Evolution
From its inception in the late 20th century to its widespread adoption in the 21st century, telemedicine has evolved significantly, driven by advances in telecommunications and information technology.
The Impact of Telemedicine
Enhancing Access to Healthcare
Telemedicine bridges geographical barriers, particularly benefiting underserved and rural populations by granting them access to specialist care and medical expertise.
Improving Patient Outcomes
Studies indicate that telemedicine interventions lead to improved patient outcomes, including reduced hospital admissions, shorter recovery times, and better management of chronic conditions.
Cost-Efficiency
By minimizing the need for physical infrastructure and streamlining healthcare delivery processes, telemedicine offers cost-effective solutions for both patients and healthcare providers.
Telemedicine Technologies
Teleconsultation Platforms
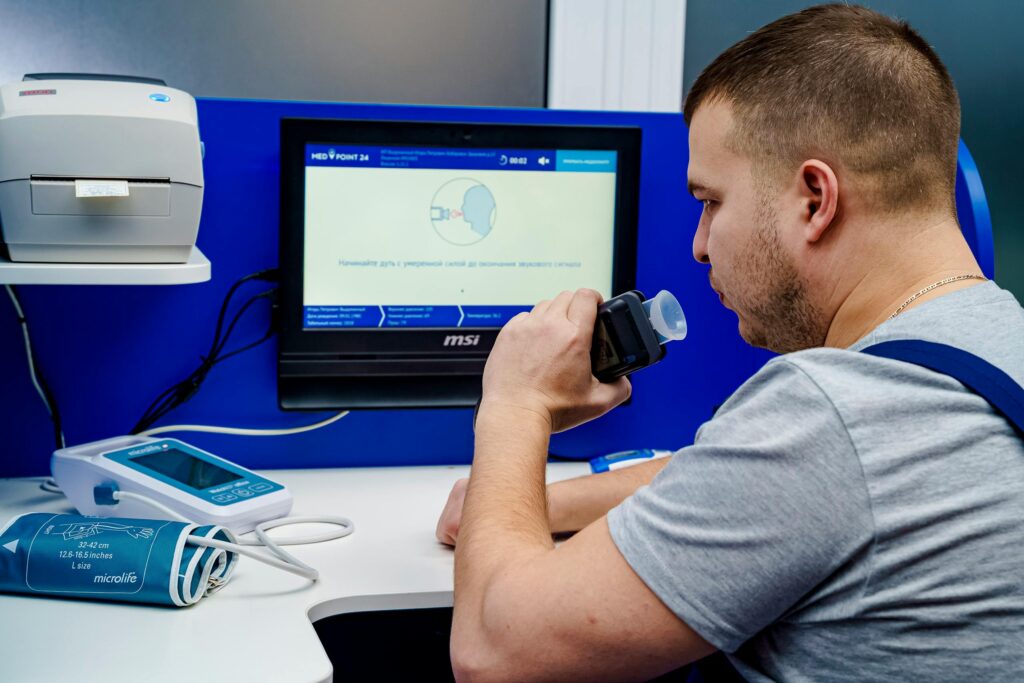
Telemedicine platforms facilitate real-time video consultations between patients and healthcare professionals, enabling seamless communication and diagnosis.
Remote Monitoring Devices
Incorporating wearable sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) technology, remote monitoring devices enable continuous tracking of vital signs and health metrics, empowering patients to proactively manage their health.

Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Licensing and Credentialing
The licensure and credentialing of healthcare providers practicing telemedicine vary across jurisdictions, posing challenges in ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Data Security and Privacy
Maintaining patient confidentiality and data security is paramount in telemedicine, necessitating adherence to stringent privacy regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act).
Challenges and Barriers
Technological Barriers
Unequal access to high-speed internet and digital devices impedes the widespread adoption of telemedicine, particularly in rural and remote areas.
Reimbursement Policies
Inconsistent reimbursement policies and limitations in insurance coverage pose financial challenges for healthcare providers offering telemedicine services.
Patient Acceptance and Engagement
Skepticism and reluctance among some patients towards virtual healthcare encounters underscore the importance of education and awareness initiatives to foster acceptance.
Future Trends and Prospects
Integration of AI and Machine Learning
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning hold promise for enhancing telemedicine capabilities, enabling predictive analytics and personalized treatment recommendations.
Expansion of Telepsychiatry and Mental Health Services
Telemedicine is poised to play a pivotal role in addressing the growing demand for mental health services, offering remote counseling and therapy sessions to individuals in need.

Global Adoption and Standardization
Efforts towards global adoption and standardization of telemedicine practices are underway, facilitated by international organizations and collaborations.
The rise of telemedicine represents a paradigm shift in healthcare delivery, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve access, efficiency, and patient outcomes. Despite inherent challenges, the ongoing evolution and adoption of telemedicine technologies hold the potential to revolutionize the way healthcare is delivered and experienced globally.
Telemedicine, with its ability to transcend geographical boundaries and connect patients with healthcare professionals regardless of location, has emerged as a beacon of hope for individuals seeking timely medical advice and treatment. As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, the future of telemedicine holds tremendous potential for revolutionizing healthcare delivery on a global scale.
Leveraging AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms are poised to revolutionize telemedicine by augmenting diagnostic accuracy and personalized treatment recommendations. These technologies analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and trends, enabling healthcare providers to make informed decisions and deliver tailored care to individual patients.
Addressing Mental Health Needs
The rise of telepsychiatry and virtual mental health services signifies a pivotal shift in addressing the growing demand for mental health support. By offering remote counseling and therapy sessions, telemedicine provides individuals with convenient access to mental health professionals, fostering early intervention and support for those in need.
Ensuring Global Standardization
Efforts towards global adoption and standardization of telemedicine practices are essential for ensuring interoperability and quality of care across borders. International organizations and collaborative initiatives play a crucial role in developing guidelines, protocols, and regulatory frameworks to govern telemedicine practices and uphold patient safety and privacy standards.

Telemedicine improves access to healthcare services in rural communities by connecting patients with specialists located elsewhere, overcoming geographical barriers. Insurance coverage for telemedicine services varies depending on the provider and policy. While many insurers now offer coverage for telehealth visits, the extent of coverage may vary. Research suggests that telemedicine consultations are comparable to in-person visits in terms of diagnostic accuracy, treatment efficacy, and patient satisfaction. Telemedicine can address a wide range of medical conditions, including acute illnesses, chronic diseases, mental health disorders, and preventive care services. Telemedicine platforms adhere to strict data security protocols, ensuring the confidentiality and privacy of patient information in compliance with regulatory standards. Telemedicine facilitates remote triage, consultation, and coordination of care during disaster scenarios, enabling timely medical assistance and resource allocation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rise of telemedicine represents a transformative shift in healthcare delivery, driven by technological innovation and a commitment to improving patient outcomes. By harnessing the power of telemedicine, we can bridge the gap between patients and healthcare providers, ensuring equitable access to quality healthcare services regardless of location or circumstance. As we embrace the possibilities of telemedicine, let us continue to advocate for its widespread adoption, recognizing its potential to shape the future of healthcare for generations to come.